Signal
Signal handles SME Connect's WebRTC Connections. These connections allow peers from different devices to communicate with each other using a peer-to-peer protocol. For on-site users and remote experts, these connections can be both video and audio. For Tools connected to the Tools Gateway, these connections are typically video or data streams.
This documentation is ordered int two main ways: API Docs & Signal Functions.
API Docs | Link
API Docs contains information about the main endpoints and services in signal. This includes:
- Logging into Signal
- Getting an Ice Server
- Sending an Offer
- Getting an Offer
- Sending an Answer
- Getting an Answer
- Expiring an Answer
- Logging out of Signal
Logging into Signal | Link
The login process occurs once a user has a valid JWT token provided by the authn service. When a user logs into SME Connect, the signal login endpoint will create a valid service session and return a session cookie to the user. This cookie is valid for a 2 hour window. The session cookie stores the user's credentials, which will provide authorization for interacting with the different signal services, such as sending/receiving offers and answers.
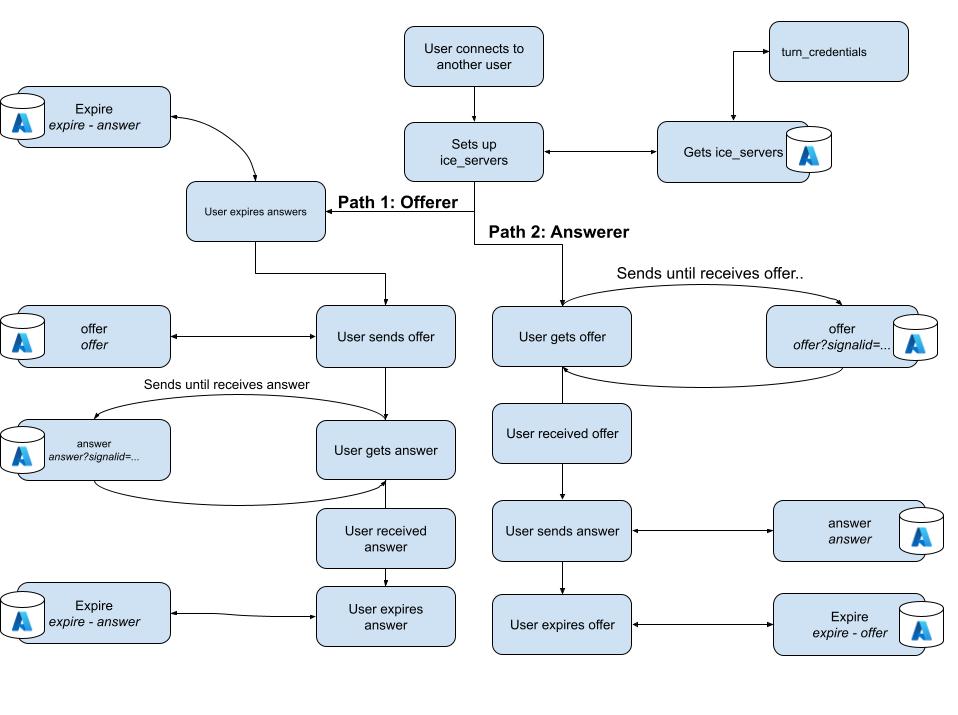
Diagram of Signal Process
The Signal service involves three main endpoints ice_servers, offer, and answer. These endpoints are what allow users to make peer-to-peer connections with each other.
Ice Servers | Link
For two peers to connect, they need to provide an ICE (Internet Connectivity Establishment) server configuration. For SME Connect, these are provided by the TURN-server through the ice_servers endpoint. This transferring of ICE candidates is often referred to as signaling, and is needed for two peers to share how they should connect.
Offer | Link
One user will send the initial offer to their peer. This offer will provide the SDP information for the user to make a successful connection with them. While the user is sending an offer to their peer, their peer will be making get requests for their peer's offer. They will continue to make get requests until they receive their peer's offer.
Answer | Link
Once the peer receives the user's offer, the peer will then send their answer to the user. This answer will contain their SDP information. The user will continually send answer requests until they receive their peer's response. Once, received, the WebRTC connection will have successfully been made and the users will expire their offers/answers.
SRC Directory: Signal's Main Functions | Link
In the Signal Repository, the SRC directory contains the service's main functions outside of the API endpoints. These are shared functions across different signal endpoints and handle actions such as adding/updating/getting database requests and processing SDPs.
Here is a list of important terminology for Signal and these functions:
- WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication): Enables real-time audio, video, and data communication directly within web browsers and native applications.
- Signaling: The server used to establish and manage communication between peers before media transfers begin.
- Data Channels: Allows browsers to send data in real-time beyond audio and video. The Digital multimeter (DMM) will send data such as temperature, currency, or voltage readings to users.
- Media Streams: The media (audio, video) flowing between peers
- ICE Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) Server: ICE manages the process of establishing connections by finding the best way for two devices to communicate directly.
- TURN (Transversal Using Relays around NAT): TURN servers act as relays when direct connections between peers are not possible due to firewalls or Network Address Translators (NAT). TURN ensures that communication between peers can still occur despite potential network issues.
- SDP (Session Description Protocol): A standard for describing the multimedia capabilities and requirements of a connection.It contains the codec (program/algorithm/device that encodes or decodes a data stream), source addressing, and timing information of audio/video.
Editing the Documentation
This documentation is created using docusaurus. This website builder has been setup to combine files containing OpenAPI configurations and TypeDoc.
The documentation files can be found in the docs directory in this repository's source files. When editing these files, do not change the file names as docusaurus has been set up to find and use these file names. The following list highlights what is contained in each file and what contents should be updated/edited when updating the documentation.
- docusaurus.config.ts
- This configuration file contains the metadata and configuration settings for creating the docusaurus website. It also includes the navigation settings. If copying this repository, update only the title property with the name of the service.
- index.md
- This file is the homepage information for the documentation. If copying this repository, edit the entire contents of this file.
- indext.ts
- This file contains the entry points for
TypeDocto compile the documentation for the exported functions/classes. If editing or adding additionalTypeDoccomments to functions and classes, check that the files are included inindex.ts. If copying this repository, edit the entire contents of this file.
- This file contains the entry points for
- openapi.yaml
- This file is the
OpenAPIstandard for the service's API. It contains information about endpoint's actions, requests, and responses. When editing or adding an endpoint, edit this file to reflect any changes made. If copying this repository, edit the entire contents of this file.
- This file is the
- typedoc.json
- This file contains the
TypeDocconfiguration used to compile and generate the documentation for this repository's functions and classes. When editing this file, edit only thename.
- This file contains the
- typedocIntro.md
- This file contains the introductory information for the
TypeDocsection of the documentation. This section highlights information about the service's functions and classes used. If copying or editing this repository, edit only thenameproperty.
- This file contains the introductory information for the
- assets
- This folder contains images that can be used in the
typedocIntro.mdandindex.mdfiles. Reference a relative URL path of:img/[FILE PATH]for Docusaurus to adequately find the image.
- This folder contains images that can be used in the
Documentation Resources
To understand more about this documentation and the resources used to compile it, consult the following resources:
- Docusaurus.io - The main website compiler.
- OpenAPI - The OpenAPI standard used to create the API documentation
- TypeDoc - The TypeScript documentation generator. It uses comments in files to create documentation